Local AI Lab Setup: Windows (WSL2 + Ollama)
This series treats your local LLM as a real service, which means the runtime has to be stable before you measure anything. On Windows, the most predictable path is WSL2 because it mirrors the Linux runtime used throughout the series.4 We are not reproducing the full install documentation here; we are giving you the shortest path to a verified endpoint. That keeps the series consistent across platforms and easy to repeat. Get the service running, then return to the main article.

Install WSL2 (Ubuntu)
Install WSL2 using the official Microsoft guidance.1 This gives you an Ubuntu shell that behaves like the Linux environment used in the rest of the series. Once WSL is installed, you can follow the Linux install guide inside that shell.2 The goal is a local Ollama service, not a Windows-native port. When that service starts, move to verification.
wsl --install
Reboot when prompted, then open Ubuntu from the Start menu.
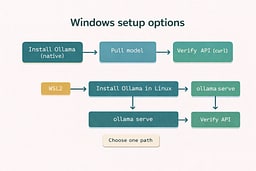
Install Ollama inside WSL
Follow the Linux install guide from inside your WSL shell so you get the correct binaries and service flow.2 If your WSL distro doesn't use systemd, you can run the server manually from the terminal. The outcome is the same: a local service on port 11434. Keep the server running while you test. Then verify the API.
Start the local service
Start the local server inside WSL and keep it running while you test. If you use systemd inside WSL, start it the same way you would on Linux. If not, run the server directly from the terminal. Either way, the endpoint should respond on localhost. Once it does, you are done with setup.
Pull a model and verify
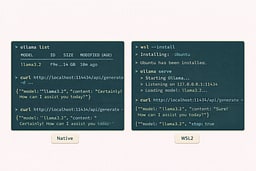
Pull a small model, run it once, then verify the HTTP endpoint from WSL.3 The real check is that the API responds with a streamed result. Once it does, the rest of the series behaves exactly like Linux. This is the moment the service boundary becomes real. After that, everything is just client code.
curl http://localhost:11434/api/generate \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "llama3.2",
"prompt": "Say hello to my little friend."
}'
You can also call http://localhost:11434 from Windows tools when WSL2 port forwarding is enabled (the default on modern Windows).
Common issues
- Connection refused: make sure
ollama serveis running in WSL. - Port access from Windows: if
localhostdoes not work, use the WSL2 IP fromwsl hostname -I.
Next
Return to the main article for streaming clients and TTFT/throughput measurement:
Sources
[1] Install WSL